10 Characteristics of Life: We explain to you what life is and what is the smallest unit in a living being. Also, its levels of organization and general characteristics.
From biology, it has been classically defined as a living being that which is capable of being born, developing, reproducing and dying.
So that life would be understood as the set of those capacities. Human life, however, is often seen as a broader concept, with highly complex philosophical components.
Almost all living things increase in size over time, a phenomenon called growth. At the same time, more or less deep and evident changes are taking place along this time, which we will analyze later.
On the other hand, living beings need to obtain energy to carry out their vital functions. That energy can come from the sun in the form of photons, or it can come from the degradation of nutrients contained in food.
Characteristics of life:
- Minimum unit: the cell
In addition to cells, there are important sub-cellular structures.
It is accepted that the smallest organizational unit in a living being is the cell, even though it is clear that important sub-cellular structures exist. This characteristic was intensely debated after the discovery of viruses, parasites consisting of just one molecule of deoxyribonucleic or ribonucleic acid surrounded by a protein cap.
- Different levels of organization
Life can present itself with a very elementary level of organization, as is the case, for example, with bacteria (unicellular beings that reproduce by simple binary fission). Even with high levels of complexity, with the presence of different types of tissues, especially suited to perform specific functions.
- Different structures
Very different structures involved in life. For example, a higher animal has, in addition to tissues, organs; a plant also. An insect comes in the form of a larva and then as an adult, completely different from each other.
- Growth and development
Metamorphosis is a paradigmatic case of vital development, characteristics of life.
Almost all living things increase in size over time, a phenomenon called growth. In turn, more or less profound and evident changes take place over this time. Often these changes are related to sexual maturity, this is called development. The metamorphosis experienced by insects is a paradigmatic case of vital development.
- Energy
Every living thing needs to obtain energy to carry out its vital functions. That energy can come from the sun in the form of photons, or it can come from the degradation of nutrients contained in food.
- It depends on a metabolism
In order for nutrients to be useful in terms of energy and as chemical skeletons, every living being must have processing molecules or enzymes, which are what ensure the biochemical processing that leads to the permanent degradation and synthesis of compounds.
- Involves adaptation phenomena
The thick leaves of the cactus prevent too much water from being lost.
Through millions of years of evolution, living beings have adapted to the environments in which they live and the availability of food.
A classic example is the giraffe, an animal that with its long neck can reach the leaf canopy of higher trees, from which it feeds. Another example is the cactus that grows in desert areas. Which thanks to the thick cover of its leaves prevents too much water from being lost.
- Irritability or excitability
This phenomenon refers to the ability to react to certain stimuli. For example, pollinating insects attracted by the colors of flowers, sunflowers orient their flowers by following the path of the sun; sneezing is often a reaction to a respiratory toxicant.
- It is self-perpetuating
In sexual reproduction there is a combination of gametes.
Every form of life has at least one mechanism for reproduction and perpetuation, some have more than one. The mechanisms are usually classified as sexual or asexual. Depending on whether or not there is a combination of gametes and thus genetic material.
- Genetic and environmental determinants
Life depends on the information contained in genes. Which is inherited from generation to generation. But also on the restrictions imposed by the surrounding environment, and this is generally the basis of evolution.

Life
The term life from biology, refers to that which distinguishes:
- Animals.
- Plants.
- Mushrooms.
- Protists.
- Archaea and germs from the rest.
It implies the capacities of organization:
- Growth.
- Metabolism.
- Response to external stimuli and reproduction.
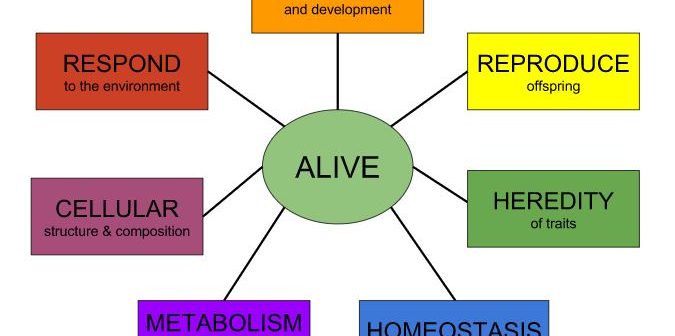
All living organisms have several key characteristics or functions:
- Order.
- Sensitivity or environmental response.
- Reproduction, growth and development.
- Regulation, homeostasis, and energy processing.
When considered together, these characteristics serve to define life.
Related posts: